Statistics
The Expatriation List: Misunderstood But Important US Tax Policy Guide

A “List” of US citizens who have chosen to renounce their citizenship has some shortcomings as a measure but is nevertheless a “Canary in the coal mine” in highlighting a desire by a significant number of people to quit the US, often for tax purposes. This article explains the system.
An occasional contributor (see an example here) to these pages is David Lesperance JD, of Lesperance Associates. Based in Canada, he comments here about topics such as expatriation, cross-border matters as they affect HNW migration, tax, and other related areas. In this article, he examines in detail the phenomenon of HNW US citizens leaving the country. For perhaps understandable reasons, it is not a subject that is a popular one. But like the figures of internal migrations within the US – such as people leaving California to go to Texas and Florida – it is worth commenting on..
The editors are pleased to share these views; the usual disclaimers apply to comments from outside contributors. To jump into the debate, email tom.burroughes@wealthbriefing.com
One topic the US government doesn’t like to draw too much attention to is the number of wealthy US citizens and long-term Green Card holders who have decided to legally and permanently leave the US tax system.
How do we know this? First, the government has set up some very effective hurdles to slow down, discourage or even prevent American taxpayers from exercising their right to leave.
Second, the government only publishes the names of a fraction of departed taxpayers long after the time they have triggered their departure. Third, the government provides no additional information or breakdowns that might help anyone actually figure out why and when these taxpayers left. And finally, there is no information on the wealth or prior tax contribution levels of these permanently departed former taxpayers. In short, they make it virtually impossible to estimate the loss of annual future tax revenues to the US Treasury arising from these departures.
While complete information is not publicly available, a Canary in the Coal Mine is the Quarterly Publication of Individuals Who Have Chosen to Expatriate List. (“the List”). The List is the report that is published every quarter as required by 26 US Code § 6039G – Information on individuals losing United States citizenship.
Who’s included on “The List”
At first glance one would reasonably assume that the List
includes every US taxpayer who is leaving the US tax system.
Sadly, this is not the case. In reality, the List only contains
some of the names of the former taxpayers…namely those who the US
government considers “wealthy”…which they define as having:
-- a net worth in excess of $2 million; or
-- a five-year average annual US federal tax
liability in excess of $190,000 (indexed for 2023).
Interestingly, the US government does include on the List:
-- those former taxpayers who fail to certify their US tax
compliance for the five years before departure.
Those departing citizens and Green Card holders who set off any one of these three triggers are classified as “covered expatriates.”
Amazingly, the List does not include:
-- US citizenship renunciations which are not covered
expatriates;
-- Green Card relinquishments which are not
“long-term” (i.e. eight out of 15 years) no matter their net
worth or prior federal tax contributions; or
-- Long-term resident relinquishments whether or not
they are covered expatriates.
As a result of these shortcomings it is not possible to determine the total lost tax revenues each year from departed taxpayers because there is no indication whether a covered expatriate is worth $2 million or $200 million or more; and long-term Green Card holders who trigger the covered expatriate thresholds are not publicly reported at all!
Accurate?
So what does the government report [do]…and is what it reports
helpful in understanding US expatriation?
Covered Expatriates on The List as Reported Each Quarter
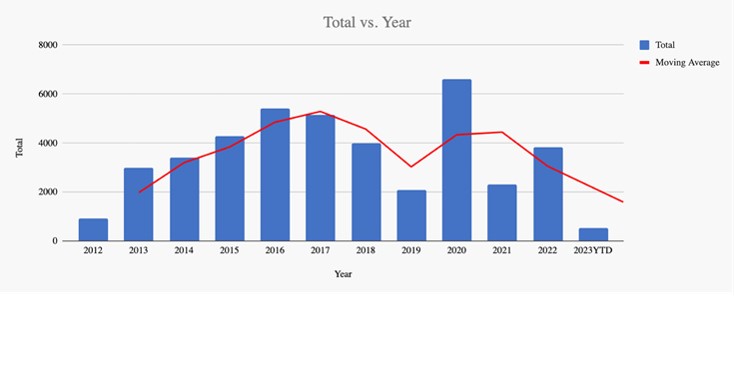
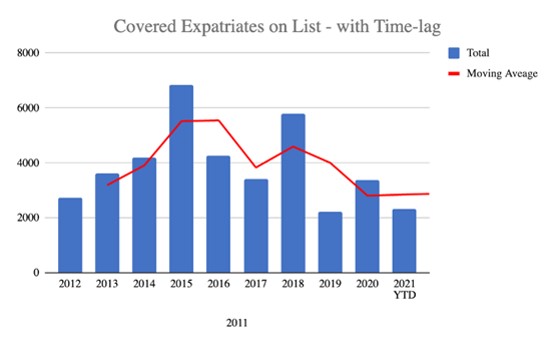
These bar charts show what is reported and conceptually illustrate the number of departing taxpayers. I say “conceptually” because neither the IRS nor the State Department provide any numbers for who is not on the List…so the chart does show how many departed taxpayers exist in reality. The only numbers on this chart are the number of Americans who have renounced citizenship and who are covered expatriates.
Another common misconception regarding the List is the timeframe between the date the former taxpayer triggered their departure and the date their names appeared on the List. Most people assume that the List reflects the covered expatriates who departed during the preceding quarter. However, based on tracking my clients, I can confidently say that the average time lag between expatriating and reporting is actually between 12 and 18 months…and sometimes as long as two or more years if the departed taxpayer left early in the year and then triggered legal tax filing extensions.
In addition to the IRS filtering who’s on the List by citizenship and wealth and the time lag limitation, there are other factors that also impact the number of names that are reported each quarter in the List.
Structural/internal factors within control of the US Government:
-- The State Department artificially restricts the number
of renunciation appointments that are available at a given US
mission;
-- Not all US missions perform renunciations;
-- Closure of missions in 2021 and 2022 due to the Covid
pandemic; and
-- Temporary re-allocation of mission staff due to local or
regional issues
External factors:
-- Government policies, like the Foreign Account Tax
Compliance Act (FATCA) that motivated foreign-based US citizens
of all financial levels to renounce their US citizenship; and
-- Concerns among HNW American taxpayers such as populist
tax proposals, gun violence, political polarization/deadlocks and
increased violence against specific groups.
What events explain the different numbers in different periods?
2010 to 2014
FATCA was passed in 2010. This resulted in financial institutions
around the world reaching out to all of their customers to
determine whether or not they were US citizens or Green Card
holders. The total number of account holders who were thereby
motivated to give up their US citizenship or Green Cards
accelerated exponentially over the next five years. While only a
small percentage of these departing taxpayers met the net worth
or federal tax paid thresholds, the total number of these covered
expatriates who renounced US citizenship (i.e. those included on
the List) also increased every year.
2015 to 2019
As the FATCA surge slowed by 2015, wealthy Americans (aka future
covered expatriates) became concerned about “Tax the Rich”
rhetoric coming from Democratic primary candidates Senators
Warren and Sanders and renounced their citizenship as they
anticipated a potential/probable Clinton POTUS victory.
When the Democratic victory did not occur, the numbers on the list dropped in 2016 and 2017. However, they increased dramatically in 2018 as a new group of wealthy Americans – concerned more about increasing political polarization and societal unrest and less about increased taxation – decided that they were bearish on the future of the US.
The drop in 2019 may have a number of explanations, but the one where we have direct knowledge relates to the handful of State Department staff who process the confirmations of US citizenship renunciations….they were redirected to deal with emergency visa issuance to victims of the earthquake in Haiti who were still recovering from a major hurricane two years prior.
2020 to 2022
In 2020 the numbers on the List increased as State Department
staff returned to process the 2019 backlog. However, new US
citizenship renunciations fell off a cliff after most US missions
closed after Q1 as a result of the Covid pandemic. This reduction
carried on in 2021, although a handful of US missions (e.g.
Queenstown New Zealand) remained open.
2023 to 2024
There will be a marked increase in the numbers on the List as US
missions began to reopen in late 2022 and again offer
renunciation appointments. We are already seeing a dramatic
increase in the number of our clients who are finally able to
complete the expatriation process after not being able to do so
during the pandemic.
On April 19, 2023, the List for the first quarter of 2023 was published with 536 individuals named. Since this is only one quarter, it is most meaningful to look at this number with a wider lens. With the time lag factored in the 2020 year to date versus 2021 year to date was up 21 per cent.
A significant recent trend is HNW Americans acquiring the ability to expatriate by setting up backup plans. These backup plans include acquiring the “fire insurance” in the form of a second citizenship and designing a “fire escape plan” to efficiently deal with the tax ramifications of being a covered expatriate.
Election Day 2024 and beyond
Whether HNW Americans actually trigger their fire escape plans
will depend upon a) tax the rich rhetoric during the 2024
primaries and campaign; b) the 2024 election outcome; and c) new
tax policies passed in the next administration.
Conclusion
The List is flawed in many ways. Even so, it can provide useful
guidance and information on expatriations by mostly wealthy US
citizens and Green Card holders in response to economic and
fiscal forces, campaign rhetoric and government policy – both
intended and unintended.
In our view, the List is a “Canary in the Coal Mine” that helps us answer the long-standing question whether wealthy American citizens and Green Card holders will overcome “life inertia” and permanently leave the US tax regime. With the top 1 per cent of US taxpayers (aka; covered expatriates) accounting for 40 per cent of the total annual US personal tax collections, this is a canary worth watching.